GDP: Understanding Its Role In Global Economies And Everyday Life
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is one of the most critical economic indicators used to measure the health and performance of a country's economy. It represents the total monetary value of all goods and services produced within a nation's borders over a specific period, typically a year. GDP provides a snapshot of economic activity, helping policymakers, businesses, and individuals make informed decisions. From determining economic growth to influencing monetary policies, GDP serves as a cornerstone for understanding the financial well-being of a country. Its relevance extends beyond economists, as it impacts everything from job opportunities to the cost of living.
For anyone seeking to understand global economies, GDP is an indispensable tool. It is not just a number but a reflection of productivity, innovation, and overall economic progress. Countries with higher GDPs often enjoy better infrastructure, healthcare, and education systems, while lower GDPs can signal economic struggles. Understanding GDP is essential for grasping how economies function and how they compare on the global stage. By analyzing GDP trends, experts can identify patterns, predict future growth, and address potential challenges.
In today’s interconnected world, GDP plays a pivotal role in shaping international relations and trade agreements. It influences investment decisions, attracts foreign capital, and determines a nation's standing in the global economy. Whether you are a student, investor, or policymaker, gaining a deeper understanding of GDP can empower you to navigate economic complexities. This article explores the intricacies of GDP, answering key questions and shedding light on its significance in both macro and microeconomic contexts.
Read also:Securely Connect Remote Iot Vpc Raspberry Pi For Free A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
What is GDP?
GDP stands for Gross Domestic Product, and it measures the total economic output of a country. Essentially, it tells us how much a country is producing in terms of goods and services. This metric is expressed in monetary terms, usually in the local currency or US dollars, and is calculated annually or quarterly. GDP is divided into three main components: consumption, investment, and government spending, along with net exports (exports minus imports). These components collectively provide a comprehensive view of economic activity.
Why Does GDP Matter?
GDP is more than just a number; it reflects the overall health of an economy. A rising GDP indicates economic growth, which often leads to job creation, higher incomes, and improved living standards. Conversely, a declining GDP may signal a recession, prompting governments to intervene with fiscal or monetary policies. Investors also rely on GDP data to assess market opportunities and risks. For instance, a country with a consistently high GDP growth rate is more likely to attract foreign investments and foster innovation.
How is GDP Calculated?
There are three primary methods to calculate GDP: the production approach, the income approach, and the expenditure approach. The production approach sums up the value of all goods and services produced. The income approach adds up all the incomes earned by individuals and businesses. Lastly, the expenditure approach considers total spending by consumers, businesses, governments, and net exports. Each method should theoretically yield the same result, providing a reliable measure of economic activity.
What Are the Types of GDP?
GDP can be categorized into several types, each offering unique insights into economic performance. Nominal GDP measures economic output using current prices, while Real GDP adjusts for inflation, providing a more accurate picture of growth. Per Capita GDP divides the total GDP by the population, offering a measure of average economic output per person. Another variant is Purchasing Power Parity (PPP) GDP, which compares economic output across countries by accounting for differences in cost of living.
How Does GDP Impact Everyday Life?
GDP has a direct impact on the lives of individuals. A growing GDP often translates to more job opportunities, higher wages, and better public services. For example, when GDP rises, governments may invest more in infrastructure, healthcare, and education. On the other hand, a shrinking GDP can lead to unemployment, reduced public spending, and economic uncertainty. Understanding GDP trends can help individuals make informed decisions about careers, investments, and savings.
Can GDP Be Misleading?
While GDP is a valuable economic indicator, it is not without its limitations. One major criticism is that GDP does not account for income inequality. For instance, a country with a high GDP may still have significant disparities in wealth distribution. Additionally, GDP does not measure non-market activities like household work or volunteerism, which contribute to societal well-being. Environmental degradation and resource depletion are also not factored into GDP calculations, potentially giving a skewed view of economic progress.
Read also:Is Jay Ma The Son Of Jack Ma Unveiling The Truth Behind The Alibaba Legacy
What Are the Limitations of GDP?
GDP focuses solely on economic output and does not capture broader aspects of societal well-being. Factors like happiness, health, education, and environmental sustainability are excluded from GDP calculations. Moreover, GDP does not differentiate between productive and unproductive activities. For example, rebuilding after a natural disaster boosts GDP, but it does not necessarily improve quality of life. These limitations have led economists to explore alternative metrics like the Human Development Index (HDI) and Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI).
How Does GDP Compare Across Countries?
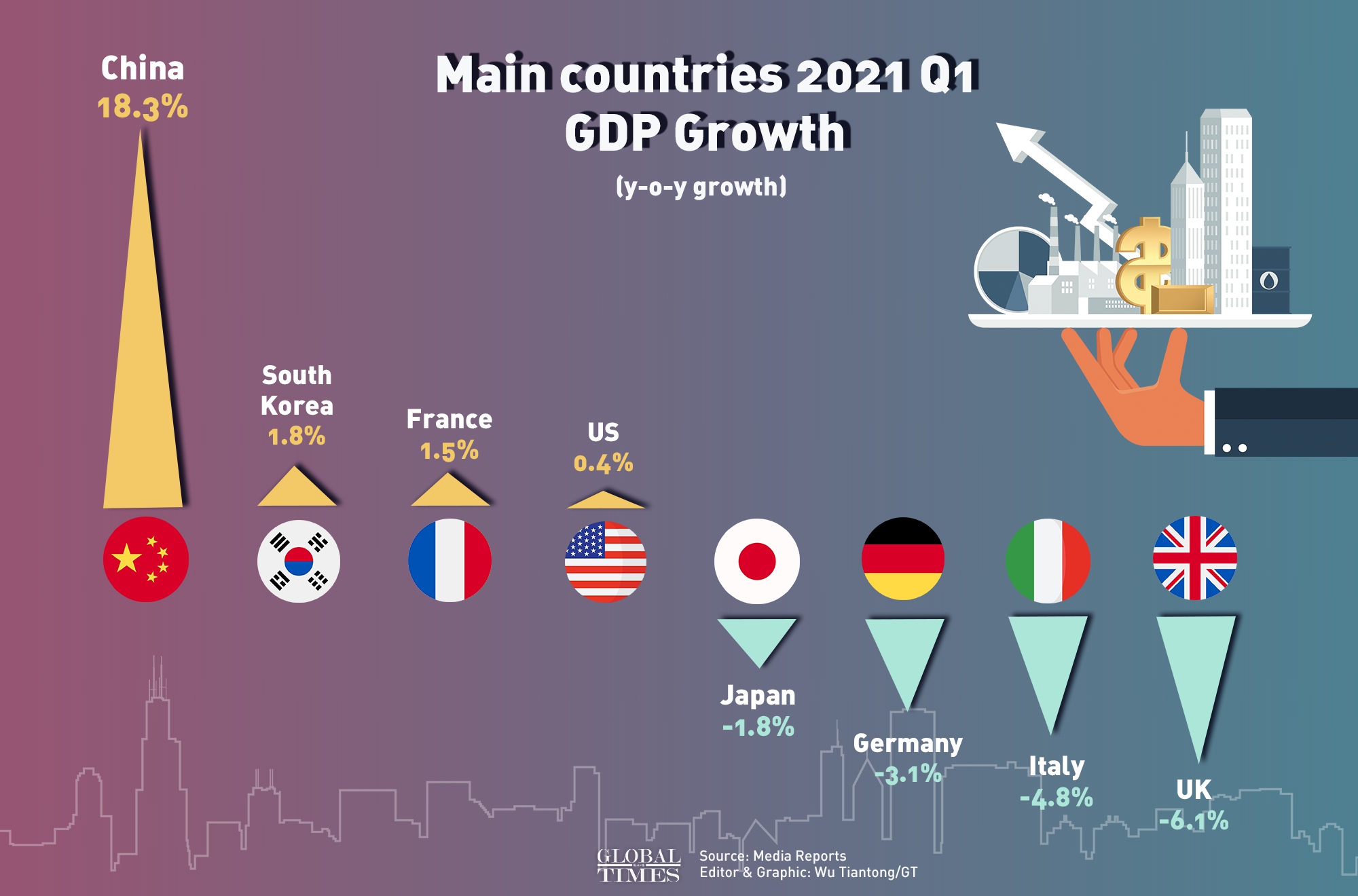
Comparing GDP across countries provides insights into global economic power dynamics. For instance, the United States has the highest nominal GDP, followed by China and Japan. However, when adjusted for PPP, China's GDP surpasses that of the US. Per Capita GDP offers another perspective, highlighting the average economic output per person. Countries like Luxembourg and Switzerland often rank high in Per Capita GDP due to their small populations and strong economies. Such comparisons help identify economic leaders and emerging markets.
What Role Does GDP Play in Global Economies?
GDP serves as a benchmark for evaluating economic performance on the global stage. It influences international trade agreements, investment flows, and foreign aid decisions. Countries with high GDPs often have greater bargaining power in global negotiations. Additionally, GDP data is used by organizations like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and World Bank to assess economic stability and recommend policy measures. Understanding GDP's role in global economies is crucial for navigating international relations and trade.
How Can GDP Data Be Used Effectively?
GDP data can be a powerful tool when used correctly. Policymakers use it to design fiscal and monetary policies that promote economic growth and stability. Businesses leverage GDP trends to identify market opportunities and risks. For individuals, GDP data can inform decisions about investments, careers, and financial planning. However, it is essential to consider GDP alongside other indicators like unemployment rates, inflation, and income distribution to get a complete picture of economic health.
In conclusion, GDP is a cornerstone of economic analysis, offering valuable insights into the performance and potential of economies worldwide. While it has its limitations, its ability to provide a standardized measure of economic output makes it indispensable. By understanding GDP and its implications, individuals and organizations can make informed decisions that contribute to economic growth and prosperity. Whether you are analyzing global trends or planning your financial future, GDP remains a key metric to watch.
The Voice 2025: A Comprehensive Guide To The Upcoming Season
Discover The Life And Legacy Of Adam Sandler: A Comedy Icon
Dortmund: Discover The Heart Of German Football And Culture
/gdp-increase-636251500-c69345ee97ba4db99375723519a2c1bd.jpg)
Real Gross Domestic Product (Real GDP) Definition
World main countries 2021 Q1 GDP Growth Global Times